Python字符串
Python中不支持char单字符类型,单字符在Python中也是一个字符串
Python字符串更新
更新Python字符串方法
1 | #!/usr/bin/python |
实际执行效果为
Updated String :- Hello Python
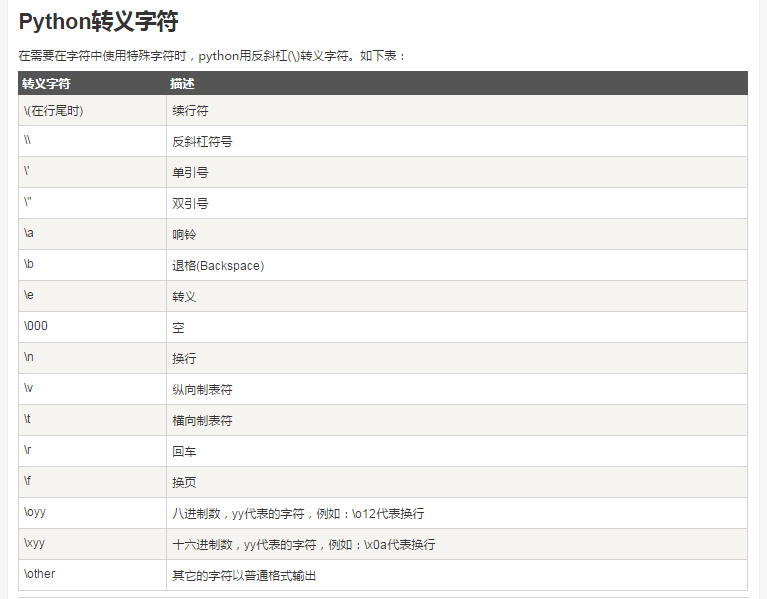
Python转义字符
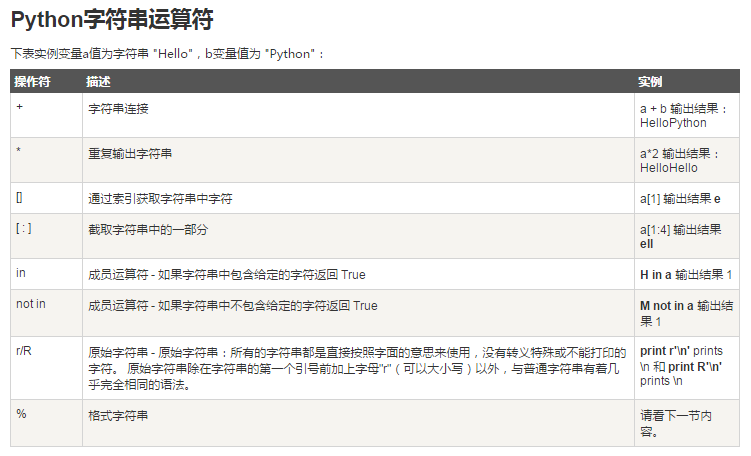
Python字符串运算符
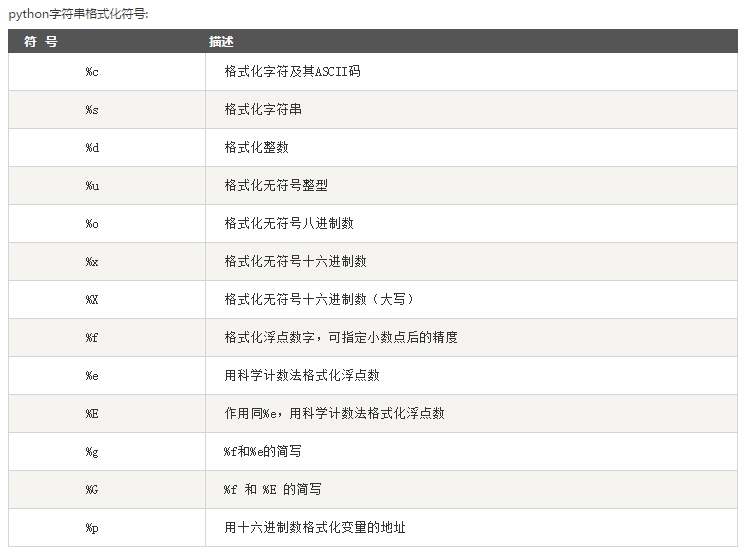
Python字符串格式化
Python三引号(triple quotes)
python中三引号可以将复杂的字符串进行复制:
python三引号允许一个字符串跨多行,字符串中可以包含换行符、制表符以及其他特殊字符。
Python字符串函数
- string.capitalize() 首字母大写
- string.count(str, beg=0, end=len(string)) 返回beg与end之间的str在string中出现的次数
- string.decode(encoding=’UTF-8’, errors=’strict’) 以encoding指定的编码格式解码string,如果出错默认报一个ValueError的异常,除非errors指定的是’ignore’或者’replace’
- string.encode(encoding=’UTF-8’, errors=’strict’) 以encoding指定的编码格式编码string
- string.endswith(obj, beg=0, end=len(string))
- string.find(str, beg=0, end=len(string)) 没有返回-1
- string.isalnum() 如果string至少有一个字符并且所有字符都是字母或数字则返回True,否则返回False
- ……
Python逻辑语句
Python条件语句
注意Python语句中的括号及语句块的使用,另外Python中没有switch语句只能使用elif替代:
1 | num = 5 |
Python循环语句
Python中支持while循环和for循环(不支持do while)。
while循环
1 | i = 1 |
如果循环体只有一条语句可以与while写在同一行
For循环
1 | for letter in 'Python': # First Example |
Python break语句
break语句打破当前循环不继续执行,如果循环嵌套,打破代码所在层的循环并执行外层循环。
Python continue
continue语句跳出本次循环,继续执行下一次循环
Python pass
pass语句是空语句,保证程序结构完整性,不做任何处理,占位
Python集合
python集合包括List、Tuple和Dictionary
Python中的List
详见python文件
- 更新list元素
1
2list1[1] = 'math'
print('list1[1]:', list1[1]) - 删除list元素
1
2del list3[len(list3) - 1]
print('list3:', list3) - Python列表脚本操作符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11print('--------Python列表脚本操作符--------')
print([1, 2, 3] + [4, 5, 6]) # list合并
print(len([1, 2, 3])) # List长度
print(['Hi!'] * 4) # 重复输出
print(3 in [1, 2, 3]) # 元素是否存在List中
for x in [1, 2, 3]: # 迭代
print(x)
L = ['spam', 'Spam', 'SPAM!']
print(L[2]) # 'SPAM!' 读取列表中第三个元素
print(L[-2]) # 'Spam' 读取列表中倒数第二个元素
print(L[1:]) # ['Spam', 'SPAM!' 从第二个元素开始截取列表 - Python列表函数&方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19test1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
aTuple = (123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc')
#
print(len(test1)) # 长度
print(max(test1)) # 最大值最小值min
print(list(aTuple)) # tuple转list
#
test1.append(7) # 在列表末尾添加新的对象
test1.count(1) # 统计出现次数
test1.extend(list(aTuple)) # 在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表)
test1.index(4) # 从列表中找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置
test1.insert(4, 4) # 将对象插入列表
test1.pop() # 移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值
test1.remove(1) # 移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项
#
print(test1)
test1.reverse()
#
# test1.sort()对原列表进行排序
Tuple特性与List相似但不能更新
Python字典(Dictionary)
字典是另一种可变容器模型,且可存储任意类型对象,如其他容器模型。
字典由键和对应值成对组成。字典也被称作关联数组或哈希表。基本语法如下:
- 访问字典里的值
1
2
3mydict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'};
print("dict['Name']: ", mydict['Name'])
print("dict['Age']: ", mydict['Age']) - 修改字典
1
2
3mydict['Age'] = 8 # update existing entry
mydict['School'] = "DPS School" # Add new entry
print('mydic:', mydict) - 删除字典元素
字典值可以没有限制地取任何python对象,既可以是标准的对象,也可以是用户定义的,但键不行1
2del mydict['Name'] # 删除键是'Name'的条目
mydict.clear() # 清空词典所有条目 - 字典内置函数&方法
详情戳这1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9dict1 = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7}
dict2 = {'Name': 'Mahnaz', 'Age': 27}
print(len(dict1)) # 计算字典元素个数,即键的总数。
print(str(dict2)) # 输出字典可打印的字符串表示
print(type(dict1)) # 返回输入的变量类型,如果变量是字典就返回字典类型。
dict3 = dict1.copy() # 返回一个字典的浅复制
dict1.clear() # 删除所有元素
print(dict3.get('Name', 'defalut = None')) # 返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值
print(dict3.keys())