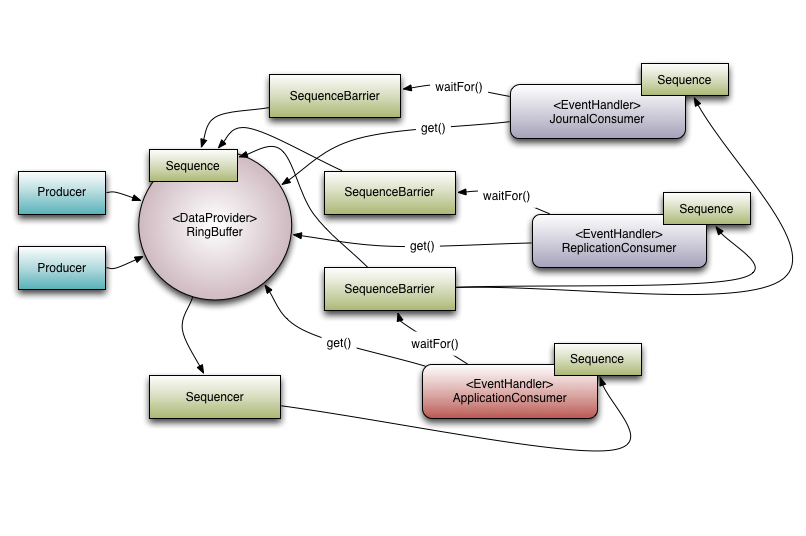
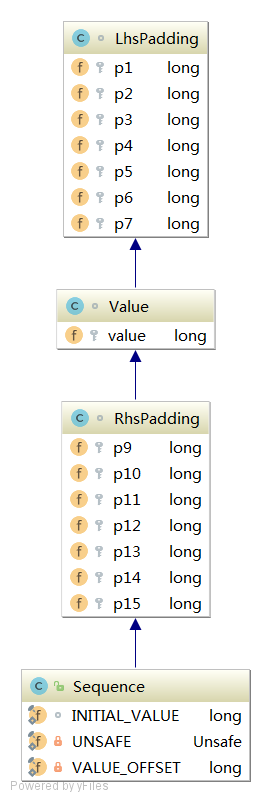
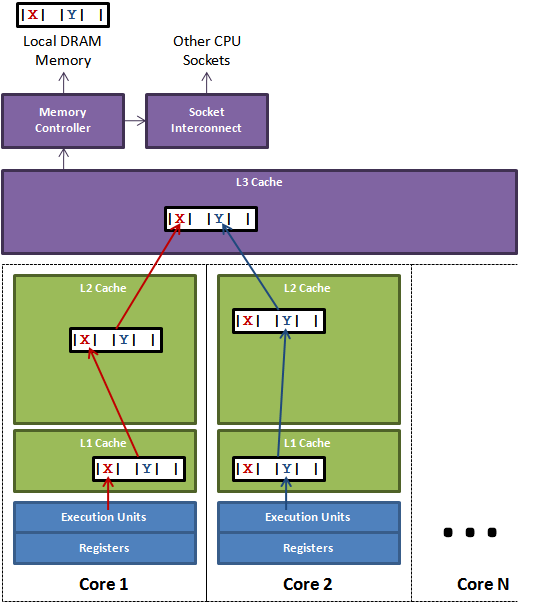
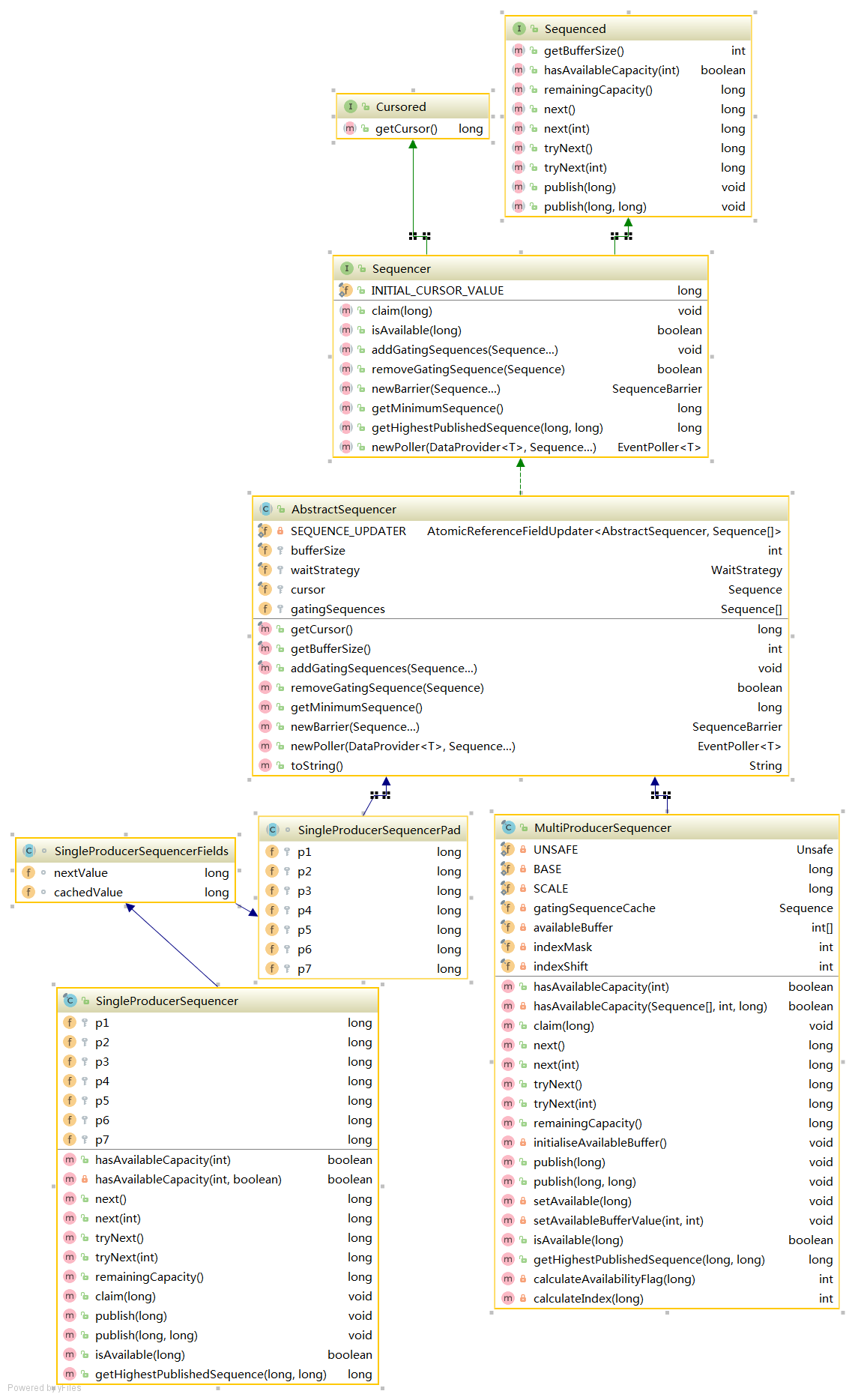
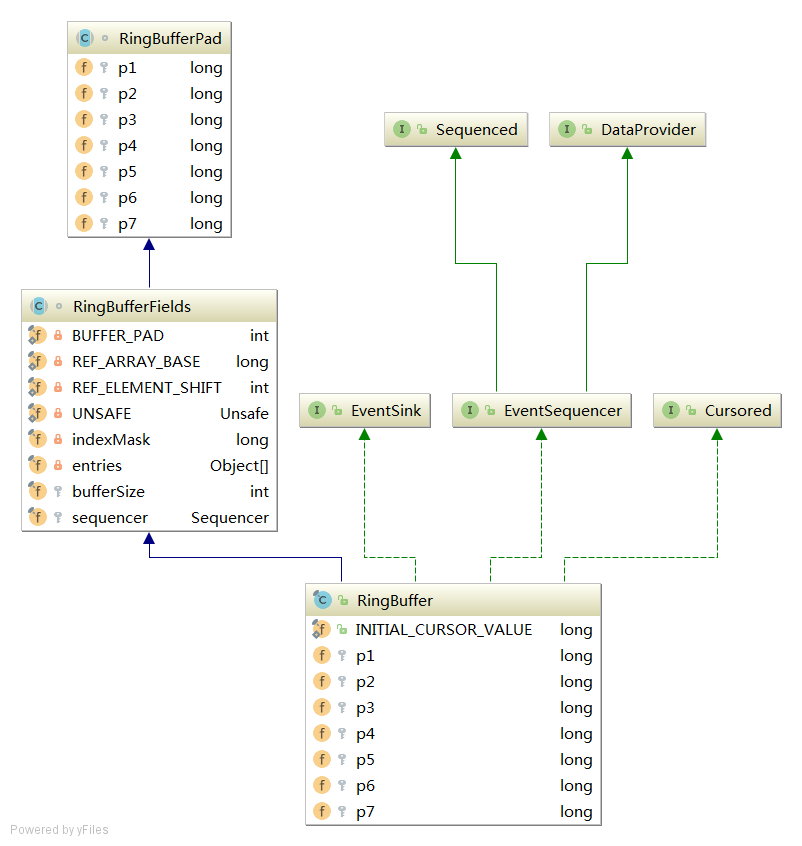
disruptor 结构
伪共享
value值始终独占一个缓存行,极限条件下为第一个或者最后一个元素,防止更新其他值时重刷导致性能下降
Sequence - AtomicLong增强(缓存行填充) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 public class Sequence extends RhsPadding { static final long INITIAL_VALUE = -1L ; private static final Unsafe UNSAFE; private static final long VALUE_OFFSET; static { UNSAFE = Util.getUnsafe(); try { VALUE_OFFSET = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(Value.class.getDeclaredField("value" )); }catch (final Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException (e); } } public Sequence () { this (INITIAL_VALUE); } public Sequence (final long initialValue) { UNSAFE.putOrderedLong(this , VALUE_OFFSET, initialValue); } public long get () { return value; } public void set (final long value) { UNSAFE.putOrderedLong(this , VALUE_OFFSET, value); } public void setVolatile (final long value) { UNSAFE.putLongVolatile(this , VALUE_OFFSET, value); } public boolean compareAndSet (final long expectedValue, final long newValue) { return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this , VALUE_OFFSET, expectedValue, newValue); } public long incrementAndGet () { return addAndGet(1L ); } public long addAndGet (final long increment) { long currentValue; long newValue; do { currentValue = get(); newValue = currentValue + increment; } while (!compareAndSet(currentValue, newValue)); return newValue; } @Override public String toString () { return Long.toString(get()); } }
Producer
Cursored接口 实现此接口的类,记录sequence位置的类。例如,生产者在生产消息时通过访问getCursor来定位当前ringBuffer下一个生产的位置,这个位置需要实时更新。
Sequenced接口 实现此接口类,实现一个有序的存储结构,也就是RingBuffer的一个特性。
getBufferSize 获取ringBuffer的大小
hasAvailableCapacity 判断空间是否足够
remainingCapacity 获取ringBuffer的剩余空间
next 申请下一个或者n个sequence(value)作为生产event的位置
tryNext 尝试申请下一个或者n个sequence(value)作为生产event的位置,容量不足会抛出InsufficientCapacityException
publish 发布Event
Sequencer接口 Sequencer接口,扩展了Cursored和Sequenced接口。在前两者的基础上,增加了消费与生产相关的方法。
INITIAL_CURSOR_VALUE: -1 为 sequence的起始值
claim: 申请一个特殊的Sequence,只有设定特殊起始值的ringBuffer时才会使用(一般是多个生产者时才会使用)
isAvailable:非阻塞,验证一个sequence是否已经被published并且可以消费
addGatingSequences:将这些sequence加入到需要跟踪处理的gatingSequences中
removeGatingSequence:移除某个sequence
newBarrier:给定一串需要跟踪的sequence,创建SequenceBarrier。SequenceBarrier是用来给多消费者确定消费位置是否可以消费用的
getMinimumSequence:获取这个ringBuffer的gatingSequences中最小的一个sequence
getHighestPublishedSequence:获取最高可以读取的Sequence
newPoller:目前没用,不讲EventPoller相关的内容(没有用到)
GatingSequence :RingBuffer的头由一个名字为cursor的Sequence对象维护,用来协调生产者向RingBuffer中填充数据。表示队列尾的Sequence并没有在RingBuffer中,而是由消费者维护。这样的话,队列尾的维护就是无锁的。但是,在生产者方确定RingBuffer是否已满就需要跟踪更多信息。为此,GatingSequence用来跟踪相关Sequence。
AbstractSequencer AbstractSequencer实现了Sequencer接口,有五个Field:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private static final AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<AbstractSequencer, Sequence[]> SEQUENCE_UPDATER =AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractSequencer.class, Sequence[].class, "gatingSequences" );protected final int bufferSize;protected final WaitStrategy waitStrategy;protected final Sequence cursor = new Sequence (Sequencer.INITIAL_CURSOR_VALUE);protected volatile Sequence[] gatingSequences = new Sequence [0 ];
该类实现了上面接口中的一些方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 @Override public final long getCursor () { return cursor.get(); } @Override public final int getBufferSize () { return bufferSize; } @Override public final void addGatingSequences (Sequence... gatingSequences) { SequenceGroups.addSequences(this , SEQUENCE_UPDATER, this , gatingSequences); } @Override public boolean removeGatingSequence (Sequence sequence) { return SequenceGroups.removeSequence(this , SEQUENCE_UPDATER, sequence); } @Override public long getMinimumSequence () { return Util.getMinimumSequence(gatingSequences, cursor.get()); } @Override public SequenceBarrier newBarrier (Sequence... sequencesToTrack) { return new ProcessingSequenceBarrier (this , waitStrategy, cursor, sequencesToTrack); } @Override public <T> EventPoller<T> newPoller (DataProvider<T> dataProvider, Sequence... gatingSequences) { return EventPoller.newInstance(dataProvider, this , new Sequence (), cursor, gatingSequences); }
SingleProducerSequencer(线程不安全) 1 2 3 4 protected long nextValue = Sequence.INITIAL_VALUE;protected long cachedValue = Sequence.INITIAL_VALUE;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 @Override public boolean hasAvailableCapacity (int requiredCapacity) { return hasAvailableCapacity(requiredCapacity, false ); } private boolean hasAvailableCapacity (int requiredCapacity, boolean doStore) { long nextValue = this .nextValue; long wrapPoint = (nextValue + requiredCapacity) - bufferSize; long cachedGatingSequence = this .cachedValue; if (wrapPoint > cachedGatingSequence || cachedGatingSequence > nextValue){ if (doStore) { cursor.setVolatile(nextValue); } long minSequence = Util.getMinimumSequence(gatingSequences, nextValue); this .cachedValue = minSequence; if (wrapPoint > minSequence){ return false ; } } return true ; } @Override public long next () { return next(1 ); }@Override public long next (int n) { if (n < 1 ){ throw new IllegalArgumentException ("n must be > 0" ); } long nextValue = this .nextValue; long nextSequence = nextValue + n; long wrapPoint = nextSequence - bufferSize; long cachedGatingSequence = this .cachedValue; if (wrapPoint > cachedGatingSequence || cachedGatingSequence > nextValue){ cursor.setVolatile(nextValue); long minSequence; while (wrapPoint > (minSequence = Util.getMinimumSequence(gatingSequences, nextValue))){ LockSupport.parkNanos(1L ); } this .cachedValue = minSequence; } this .nextValue = nextSequence; return nextSequence; } @Override public long tryNext () throws InsufficientCapacityException { return tryNext(1 ); }@Override public long tryNext (int n) throws InsufficientCapacityException{ if (n < 1 ){ throw new IllegalArgumentException ("n must be > 0" ); } if (!hasAvailableCapacity(n, true )){ throw InsufficientCapacityException.INSTANCE; } long nextSequence = this .nextValue += n; return nextSequence; } @Override public long remainingCapacity () { long nextValue = this .nextValue; long consumed = Util.getMinimumSequence(gatingSequences, nextValue); long produced = nextValue; return getBufferSize() - (produced - consumed); } @Override public void claim (long sequence) { this .nextValue = sequence; }@Override public void publish (long sequence) { cursor.set(sequence); waitStrategy.signalAllWhenBlocking(); } @Override public void publish (long lo, long hi) { publish(hi); }@Override public boolean isAvailable (long sequence) { return sequence <= cursor.get(); } @Override public long getHighestPublishedSequence (long lowerBound, long availableSequence) { return availableSequence; }
MultiProducerSequencer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private static final Unsafe UNSAFE = Util.getUnsafe();private static final long BASE = UNSAFE.arrayBaseOffset(int [].class);private static final long SCALE = UNSAFE.arrayIndexScale(int [].class);private final Sequence gatingSequenceCache = new Sequence (Sequencer.INITIAL_CURSOR_VALUE);private final int [] availableBuffer;private final int indexMask;private final int indexShift;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 public boolean hasAvailableCapacity (final int requiredCapacity) { return hasAvailableCapacity(gatingSequences, requiredCapacity, cursor.get()); } private boolean hasAvailableCapacity (Sequence[] gatingSequences, final int requiredCapacity, long cursorValue) { long wrapPoint = (cursorValue + requiredCapacity) - bufferSize; long cachedGatingSequence = gatingSequenceCache.get(); if (wrapPoint > cachedGatingSequence || cachedGatingSequence > cursorValue){ long minSequence = Util.getMinimumSequence(gatingSequences, cursorValue); gatingSequenceCache.set(minSequence); if (wrapPoint > minSequence){ return false ; } } return true ; } @Override public long next () { return next(1 ); }@Override public long next (int n) { if (n < 1 ){ throw new IllegalArgumentException ("n must be > 0" ); } long current; long next; do { current = cursor.get(); next = current + n; long wrapPoint = next - bufferSize; long cachedGatingSequence = gatingSequenceCache.get(); if (wrapPoint > cachedGatingSequence || cachedGatingSequence > current){ long gatingSequence = Util.getMinimumSequence(gatingSequences, current); if (wrapPoint > gatingSequence){ LockSupport.parkNanos(1 ); continue ; } gatingSequenceCache.set(gatingSequence); }else if (cursor.compareAndSet(current, next)){ break ; } }while (true ); return next; } @Override public void publish (final long sequence) { setAvailable(sequence); waitStrategy.signalAllWhenBlocking(); } @Override public void publish (long lo, long hi) { for (long l = lo; l <= hi; l++){ setAvailable(l); } waitStrategy.signalAllWhenBlocking(); } private void setAvailable (final long sequence) { setAvailableBufferValue(calculateIndex(sequence), calculateAvailabilityFlag(sequence)); } private void setAvailableBufferValue (int index, int flag) { long bufferAddress = (index * SCALE) + BASE; UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(availableBuffer, bufferAddress, flag); } @Override public boolean isAvailable (long sequence) { int index = calculateIndex(sequence); int flag = calculateAvailabilityFlag(sequence); long bufferAddress = (index * SCALE) + BASE; return UNSAFE.getIntVolatile(availableBuffer, bufferAddress) == flag; } @Override public long getHighestPublishedSequence (long lowerBound, long availableSequence) { for (long sequence = lowerBound; sequence <= availableSequence; sequence++) { if (!isAvailable(sequence)){ return sequence - 1 ; } } return availableSequence; } private int calculateAvailabilityFlag (final long sequence) { return (int ) (sequence >>> indexShift); } private int calculateIndex (final long sequence) { return ((int ) sequence) & indexMask; }
环形无锁队列RingBuffer
RingBuffer类中保存了整个RingBuffer每个槽(entry或者slot)的Event对象,对应的field是private final Object[] entries;这些对象只在RingBuffer初始化时被建立,之后就是修改这些对象(初始化Event和填充Event),并不会重新建立新的对象。RingBuffer可以有多生产者和消费者,所以这个entries会被多线程访问频繁的,但不会修改(因为不会重新建立新的对象,这个数组保存的是对对象的具体引用,所以不会变)
运算取模
m % 2^n = m & ( 2^n - 1 ) //RingBuffer中数组大小必须为2的倍数
源码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 abstract class RingBufferFields <E> extends RingBufferPad { private static final int BUFFER_PAD; private static final long REF_ARRAY_BASE; private static final Unsafe UNSAFE = Util.getUnsafe(); static { final int scale = UNSAFE.arrayIndexScale(Object[].class); if (4 == scale){ REF_ELEMENT_SHIFT = 2 ; } else if (8 == scale){ REF_ELEMENT_SHIFT = 3 ; } else { throw new IllegalStateException ("Unknown pointer size" ); } BUFFER_PAD = 128 / scale; REF_ARRAY_BASE = UNSAFE.arrayBaseOffset(Object[].class) + (BUFFER_PAD << REF_ELEMENT_SHIFT); } private final long indexMask; private final Object[] entries; protected final int bufferSize; protected final Sequencer sequencer; RingBufferFields(EventFactory<E> eventFactory, Sequencer sequencer){ this .sequencer = sequencer; this .bufferSize = sequencer.getBufferSize(); if (bufferSize < 1 ){ throw new IllegalArgumentException ("bufferSize must not be less than 1" ); } if (Integer.bitCount(bufferSize) != 1 ){ throw new IllegalArgumentException ("bufferSize must be a power of 2" ); } this .indexMask = bufferSize - 1 ; this .entries = new Object [sequencer.getBufferSize() + 2 * BUFFER_PAD]; fill(eventFactory); } private void fill (EventFactory<E> eventFactory) { for (int i = 0 ; i < bufferSize; i++) { entries[BUFFER_PAD + i] = eventFactory.newInstance(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected final E elementAt (long sequence) { return (E) UNSAFE.getObject(entries, REF_ARRAY_BASE + ((sequence & indexMask) << REF_ELEMENT_SHIFT)); } }
RingBuffer中方法大部分都是在包装EventTranslator以及Sequencer中的方法。
构造一个RingBuffer需要如下元素:实现EventFactory的Event的工厂,实现Sequencer的生产者,等待策略waitStrategy还有bufferSize。
EventTranslator的作用主要是发布Event,还有EventTranslatorTwoArg,EventTranslatorVararg等有类似作用
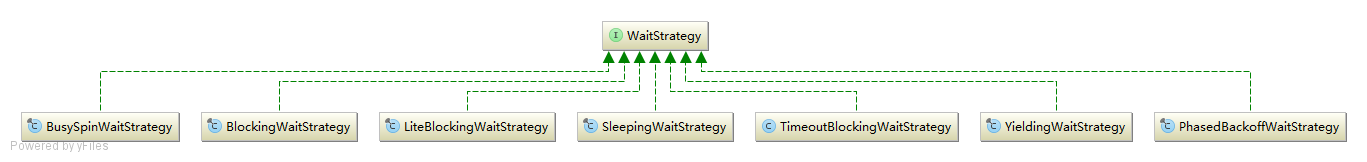
WaitStrategy
BlockingWaitStrategy:通过线程阻塞的方式,等待生产者唤醒
BusySpinWaitStrategy:线程一直自旋等待,比较耗CPU。
LiteBlockingWaitStrategy:通过线程阻塞的方式,等待生产者唤醒,比BlockingWaitStrategy要轻,某些情况下可以减少阻塞的次数。
PhasedBackoffWaitStrategy:根据指定的时间段参数和指定的等待策略决定采用哪种等待策略。
SleepingWaitStrategy:可通过参数设置,使线程通过Thread.yield()主动放弃执行,通过线程调度器重新调度;或一直自旋等待。
TimeoutBlockingWaitStrategy:通过参数设置阻塞时间,如果超时则抛出异常。
YieldingWaitStrategy: 通过Thread.yield()主动放弃执行,通过线程调度器重新调度。
waitStrategy接口 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public interface WaitStrategy { long waitFor (long sequence, Sequence cursor, Sequence dependentSequence, SequenceBarrier barrier) throws AlertException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException; void signalAllWhenBlocking () ; }
BlockingWaitStrategy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public final class BlockingWaitStrategy implements WaitStrategy { private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock (); private final Condition processorNotifyCondition = lock.newCondition(); @Override public long waitFor (long sequence, Sequence cursorSequence, Sequence dependentSequence, SequenceBarrier barrier) throws AlertException, InterruptedException{ long availableSequence; if (cursorSequence.get() < sequence){ lock.lock(); try { while (cursorSequence.get() < sequence){ barrier.checkAlert(); processorNotifyCondition.await(); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } while ((availableSequence = dependentSequence.get()) < sequence){ barrier.checkAlert(); } return availableSequence; } @Override public long waitFor (final long sequence, Sequence cursor, final Sequence dependentSequence, final SequenceBarrier barrier) throws AlertException, InterruptedException { long availableSequence; while ((availableSequence = dependentSequence.get()) < sequence) { barrier.checkAlert(); } return availableSequence; } @Override public void signalAllWhenBlocking () { lock.lock(); try { processorNotifyCondition.signalAll(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
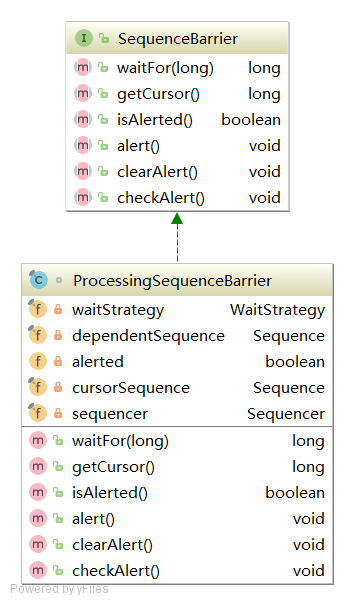
SequenceBarrier
SequenceBarrier只有一个实现类,就是ProcessingSequenceBarrier。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 final class ProcessingSequenceBarrier implements SequenceBarrier { private final WaitStrategy waitStrategy; private final Sequence dependentSequence; private volatile boolean alerted = false ; private final Sequence cursorSequence; private final Sequencer sequencer; ProcessingSequenceBarrier(final Sequencer sequencer, final WaitStrategy waitStrategy, final Sequence cursorSequence, final Sequence[] dependentSequences){ this .sequencer = sequencer; this .waitStrategy = waitStrategy; this .cursorSequence = cursorSequence; if (0 == dependentSequences.length){ dependentSequence = cursorSequence; }else { dependentSequence = new FixedSequenceGroup (dependentSequences); } } @Override public long waitFor (final long sequence) throws AlertException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException { checkAlert(); long availableSequence = waitStrategy.waitFor(sequence, cursorSequence, dependentSequence, this ); if (availableSequence < sequence) { return availableSequence; } return sequencer.getHighestPublishedSequence(sequence, availableSequence); } @Override public long getCursor () { return dependentSequence.get(); } @Override public boolean isAlerted () { return alerted; } @Override public void alert () { alerted = true ; waitStrategy.signalAllWhenBlocking(); } @Override public void clearAlert () { alerted = false ; } @Override public void checkAlert () throws AlertException{ if (alerted) { throw AlertException.INSTANCE; } } }